I keep updating my investment property tracking spreadsheet to reflect the current costs of insurance and taxes. My tracking shows last year’s amount, which I use as an indicator on whether I need to look further into this year’s bill (e.g., is the amount a reasonable increase?). For so many years, most of our insurance policies changed by a few dollars; now, I’m seeing large swings in what’s being charged. Where jurisdictions were slow to change property assessments, they’re now catching up, which increases the taxes.
As a renter, your rent is increasing to cover these costs of the landlord/owner. Here’s a comparison of my fixed cost increases against my rent rate increases. As you’ll see, I’m not trying to get top dollar out of these properties because the market has increased so much (and that leaves me more exposed if someone doesn’t pay their rent on time). My rent increases barely cover the cost increases that are happening on some of these houses. Remember that while I’m showing fixed costs, this isn’t covering the maintenance calls that I receive and how they’re more expensive than they once were also.
ESCROW, CONCEPTUALLY
In most cases, for a traditional mortgage, an escrow account is set up. It calculates your taxes and insurance payments for the year, divides by twelve, and is added to your principal and interest payment for the mortgage. In addition to covering the total payments to be made, there’s also a requirement that the balance of the account never falls below twice the required monthly payment.
If your taxes owed for a year are $1500, and the insurance is $300, then your monthly breakdown is $150 ($1500+$300=$1800; $1800/12=$150). The minimum monthly required balance is $300 (twice the $150).
As taxes and insurance increase each year (typically), there’s an analysis done to ensure the projected monthly balance never falls below that $300 threshold. If the balance is projected to fall below the required minimum amount, then it triggers an increase in your escrow payment. Your escrow payment will increase to cover the shortfall, but also to cover the new projected costs to be paid. So while you may be offered the ability to make a one-time payment to cover the shortfall, your mortgage payment may still increase to cover the projected costs. For example, if last year, your tax payment increased to $1750, and your insurance to $350, then your monthly payment to cover those charges is $175 ($1750+350=$2100; $2100/12=$175). Your mortgage will increase by $25 per month because now your escrow agent knows the projected costs to cover are higher.
The analysis uses the current year’s amounts owed to project the coming year’s monthly balances; it doesn’t account for the probability that these amounts increase each year, which essentially means that there’s perpetually a shortfall. In other words, while in Year3, they know that there was an increase in costs from Year1 to Year2, they don’t inflate the costs of Year2 to cover Year3 projected payments.
I prefer to not have an escrow, but at this point, for any mortgages we have, they’re all escrowed. We have six of thirteen houses with escrow. While I pay more as my mortgage to feed into that escrow account, it means I don’t have to manage the annual or semi-annual payments. On the contrary, this means I need to be managing our finances to prepare for large outlays throughout the year on seven houses (in the last quarter of the year, I’m paying out over $8,000 to cover taxes owed).
ESCROW REANALYSIS
This post was prompted by a notification that an escrow reanalysis was done on a mortgage that was just transferred to a new company. I thought that their break down was the most clear I’ve seen. A quick note – your escrow will pay the bills that come due, regardless of the balance in the account, even if it means it’ll overdraw the account.
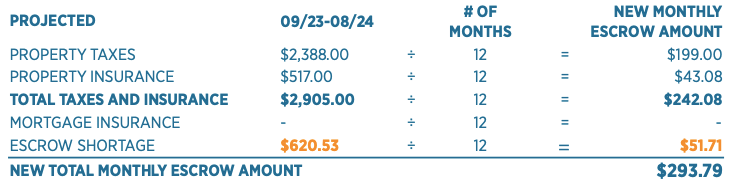
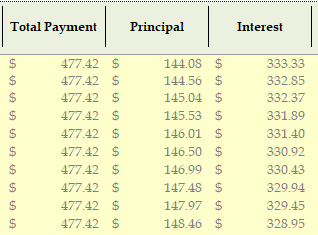
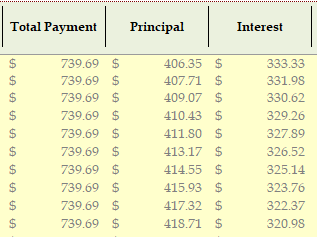
They clearly showed that the anticipated property taxes are projected at $199 per month (although, I’ll reiterate that this is based on last year’s actual outlay numbers, which aren’t accurate for the coming year). Then they show that the taxes are $43.08 per month. They then go as far to show the total of these two required outlays. There’s verbiage that explains the required minimum in the account must be twice the total taxes and insurance ($242.08 * 2 = $484.16).
There’s another detailed breakdown of each month’s escrow income and outlay (that I don’t have pictured here) that shows the month that is projected to fall below the required minimum. That month’s account balance is -$136.37. The difference between the required amount of $484.16 and the negative balance of $136.37 is $620.53 (pictured above). When that’s broken down by month, it’s $51.71. Take the total taxes and insurance payments and add the shortage amount to get the new monthly escrow amount of $293.79, a change from $222.25.
Below, they show you that there is no change in the principal and interest payment, then it shows how the current escrow payment is adjusted to the new escrow payment, along with the shortage amount.
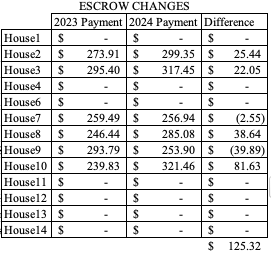
I created this table to show the differences between escrow payments over the two years. I kept the houses that don’t have an escrow because it can be compared to a future table in this post. There is no House5 in this table because we sold it several years ago (houses didn’t get renumbered because House5 still exists in terms of tax documentation).
TAX AND INSURANCE UPDATES
Each year, we see an increase in these amounts. Usually it’s across the board, but Kentucky districts had kept the housing assessments the same through the pandemic. As housing prices increase, your property assessment can be increased by your tax jurisdiction. The assessment increasing leads to an increase in taxes. This is why people getting excited that house prices in their neighborhood are selling higher than expected isn’t great if you’re not planning on selling any time soon; those increases in values means you’re paying higher in taxes.
In Richmond, VA, the property taxes are $1.20 per each $100 of the assessed value. In 2022, House2’s value $163,000. In 2023, the value was increased to $203,000. And let’s not forget that we purchased the house for $117,000. While it’s nice that the home values in the neighborhood are increasing significantly (and we knew the area was going to get better and better based on development happening), we can’t realize this gain until (and if) we sell. So in the meantime, we’re paying higher taxes on this amount. Although, I suppose the assessment could be even higher because the actual value of this house is probably more like $260,000.
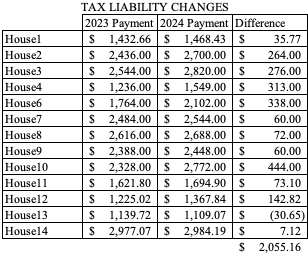
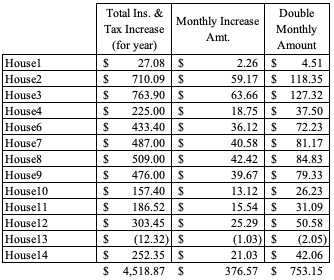
Among 13 houses (don’t get confused – there’s no House5 up there because we sold it), I need to cover a total cost increase for taxes and insurances of over $4,500. This doesn’t include the higher costs of trades people if there are any maintenance calls, so this increase is the bare minimum for me to keep my same income.
RENT INCREASES
I constantly see complaints about the cost of rent, or that a landlord is increasing rent. Unless we’re looking for a tenant to move, our general philosophy is to increase rent $50 every two years. This worked fine because home assessments increased at a slow, reasonable rate until recent years. Now jurisdictions are capturing these larger increases based on those inflated sale numbers when competition was high in from 2020 through 2022.
In some cases, the rent for the area brought it in a higher amount than compared to our purchase price of a house. In those cases, we went several years without increasing the rent. Looking back, that probably wasn’t the best idea because now we’re behind on capturing how significant these last few year’s fixed costs have increased. However, the trade off to that is that we’ve kept great tenants in the house, haven’t had to pay to turnover the unit, and have minimal maintenance calls.
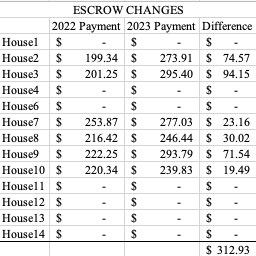
This table shows the total increase in insurance and tax payments from 2022 to 2023 in the first column. I divided that by 12 to get the monthly amount of that increase (second column). Then, since I said we typically increase our rent by $50 every two years for the same tenant, I multiplied that monthly amount by 2. I’m showing that if we want to only increase rent on long term tenants every other year, then I need to plan ahead on how much my costs are increasing.
This isn’t a perfectly accurate capturing of our cost increases since I’m not going back to 2021 to capture those changes in amounts, but it’s a general estimate. This shows that if I were to increase all houses by only $50 every two years, it’s cutting into my bottom line. Only 6 of the houses have increases less than $50 for two years.
SETTING THE RENTAL RATE
Let’s pause and talk about “bottom line.” Landlords have investment properties to make a profit. They’re looking for an income stream.
I regularly hear people say they can own a house for less than their rent, which is likely if you’re speaking only on principal and interest of a loan. However, you need to qualify for that loan. You may not have 20% down, so you may be required to pay private mortgage insurance (PMI). You may not have good credit, which means you’re probably going to pay a higher interest rate than I’m currently paying. You need to be able to cover taxes and insurance, which means you’ll have an escrow account set up, which increases your monthly mortgage payment. Then there’s all the other costs of home ownership.
That’s where people forget. When your hot water goes out, you call me. I spend $1,500 for about 2 hours worth of someone’s work to replace that. When you have a water leak, I spend $3,000 for a day’s worth of 2 plumbers’ work. When a storm drops a tree on your house, I’m the one spending hours on the phone with insurance, finding a contractor, getting quotes, and paying the contractor $3,700 before I get insurance reimbursement. Those are the big unexpected expenses. That doesn’t include all those smaller plumbing problems that cost $200 or $500 at a time.
Then in some cases, I probably put time and money into the house to even get it ready to rent to you. I didn’t always buy a house that was ready to live in. You may have projects that need to be done when you first move in also, so which costs money. Those are expenses that I’m trying to recoup through my rent rate also.
There may be other costs to my ownership that I’m trying to recoup through the rent, such as property management. I may have to pay someone else 10% of the rent, every month. I am projecting that there are going to be costs that I need to pay for also (e.g., water heater, roof replacement, plumbing issues). When I need to pay a plumber $3,000, I’m not coming to the tenant to say “I now need $3,000 to cover this cost.” Instead, I’ve set my rental rate the expect such a large payout on my part.
Not only am I trying to make sure that my rent is set at the right about to cover the costs that I’m putting into owning and maintaining the house, I’m also hoping that I’m going to make some money off owning this house so that I can live. I don’t get to pay myself for the hours I put into managing the property. Whether or not I have a property manager, there is still time that I put into managing the houses. Would you want to work for free?
BACK TO RENT INCREASES
While we manage each house individually on setting the rates (asking ourselves: do we think the tenant can absorb the increase, do we have to increase to cover actual costs now), this shows that our monthly income was increased by $475. If you look back at our total monthly increase in expenses of just taxes and insurance, it’s about $375; add in the cost increases for property management (increased rent means increased fees because fees are based on the rent price), and our fixed costs went up $415. On a whole, we’ve offset the increases.
However, you can see if we had one or two houses, some of those increases could be significant. House3 is costing us $64 more for each month, but our increases are typically about $50 at a time. We’ve had the same tenant in this house since we bought it. A $50 increase every two years hasn’t kept up with our costs. Since we have other houses, it helps cover the costs on House3.
House2 and House3 are identical in layout. House2 has been upgraded to all LVP, whereas House3 has carpet everywhere except the kitchen and bathrooms (granted, it’s new carpet two years ago). Since we purchased these two homes with tenants, rent was already set for us. House3 has been the same tenant since we bought the house, and the increases have brought us to $1200 per month in rent. House2 has been turned over 3 times: the first was a divorced lady who moved back in with her ex-husband; the second was there for several years, but we began having a lot of issues with her, and we told her the lease was up; the third was the one who flooded the house in December, and causing the need for the fourth. Now we’re renting that house at its market value of $1600. That means House3 is operating at a much lower rent than we could get if we rented to new tenants. However, the tenants are wonderful, and we’ve purposely not raised the rent on them in significant ways because we don’t want to cause them to move.
SUMMARY
Cost increases in rental properties can be significant over the years. With the rising costs of all goods and services, property values weren’t immune. The increase in property values leads to an increase in an assessment, which means an increase in taxes. That cost is relayed to the tenant, as this is a for-profit business. I’m trying to make an income for my family with rental properties.
I’m not trying to price gouge tenants, but make a fair living based on the costs of owning these houses. My first goal is to not turnover tenants, so I do what I can to make my tenants happy by taking care of the houses and not creating drastic rent increases each year. Secondly, I’m not going to set a price that my tenant can’t afford, thereby putting me in a hard position where I don’t have rent paid. Having multiple properties helps to offset the costs so I don’t have to play catch up on one or two houses worth of higher expenses, by putting my long-term tenants in an uncomfortable position where they can’t afford the rent.